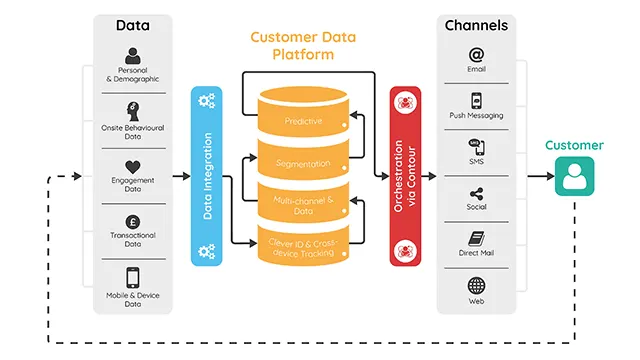
Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) have become a critical component of modern marketing and customer experience strategies. Here’s a comprehensive overview, covering what they are, how they work, benefits, key features, vendors, and future trends:
1. What is a Customer Data Platform (CDP)?
A CDP is a unified customer database that centralizes customer data from various sources to create a single, coherent view of each customer. Think of it as the “single source of truth” for your customer information.
Key Differences from other systems
- CRM (Customer Relationship Management): CRMs primarily focus on known customers and sales interactions. CDPs handle both known and anonymous data, building profiles over time. CRMs are operational; CDPs are analytical and activation-focused.
- Data Management Platform (DMP): DMPs primarily deal with anonymous data for advertising purposes (targeting and retargeting). They are often cookie-based and have limited data retention. CDPs focus on identified customers and long-term relationships.
- Data Warehouse: Data warehouses store large volumes of historical data, but aren’t designed for real-time activation or identity resolution. CDPs are built for actionable customer data.
- Marketing Automation Platform (MAP): MAPs execute marketing campaigns. They use the data from a CDP, but don’t collect and unify it.
2. How do CDPs Work?
The core process of a CDP involves these steps:
- Data Collection: CDPs ingest data from numerous sources:
- First-Party Data: Website activity, app usage, purchase history, email interactions, customer service logs, loyalty program data, offline transactions.
- Second-Party Data: Data shared directly from a trusted partner.
- Third-Party Data: Data purchased from external sources (often used for enrichment, but becoming less reliable due to privacy concerns).
- Identity Resolution: This is a crucial step. CDPs use deterministic (exact matches like email address) and probabilistic (using algorithms to infer identity) methods to link data from different sources to a single customer profile. This creates a “golden record” for each customer.
- Data Unification & Standardization: Data is cleaned, transformed, and standardized to ensure consistency. Different data formats and naming conventions are reconciled.
- Segmentation: CDPs allow you to create granular customer segments based on demographics, behavior, preferences, and more.
- Activation: This is where the value is realized. CDP data is pushed to other systems for personalized experiences:
- Marketing Automation: Triggered emails, personalized content.
- Advertising Platforms: Targeted ads on social media and search engines.
- Customer Service: Agents have a 360-degree view of the customer.
- Sales Teams: Prioritized leads and personalized outreach.
- Website Personalization: Dynamic content based on customer profiles.
3. Benefits of Implementing a CDP
- Improved Customer Experience: Personalized interactions across all channels.
- Increased Marketing ROI: More targeted campaigns and reduced wasted ad spend.
- Enhanced Customer Loyalty: Building stronger relationships through relevant engagement.
- Better Data-Driven Decision Making: A single source of truth for customer insights.
- Increased Revenue: Improved conversion rates and customer lifetime value.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlined data management and reduced data silos.
- Compliance with Privacy Regulations: Centralized data management aids in GDPR, CCPA, and other compliance efforts.
4. Key Features to Look For in a CDP
- Data Connectors: A wide range of pre-built integrations with common data sources.
- Identity Resolution: Robust and accurate identity matching capabilities.
- Data Governance & Security: Compliance with privacy regulations and secure data storage.
- Segmentation Engine: Advanced segmentation options based on various criteria.
- Real-Time Data Processing: Ability to process data in real-time for immediate activation.
- Activation Capabilities: Seamless integration with marketing and sales tools.
- Analytics & Reporting: Dashboards and reports to track customer behavior and campaign performance.
- Scalability: Ability to handle growing data volumes and user base.
- User Interface (UI): Intuitive and easy-to-use interface for non-technical users.
- API Access: For custom integrations and data exchange.
5. Popular CDP Vendors (as of late 2023/early 2024)
This is a rapidly evolving market. Here’s a breakdown of some leading players, categorized by focus:
- Leaders (Comprehensive Platforms):
- Segment (Twilio Segment): Widely adopted, strong developer focus, excellent data collection.
- Salesforce CDP (formerly Customer 360 Audiences): Deep integration with the Salesforce ecosystem.
- Adobe Experience Platform: Part of the Adobe Experience Cloud, powerful but complex.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Insights: Integrates well with Microsoft products.
- Mid-Market & Growing Platforms:
- Bloomreach: Focuses on commerce experience and personalization.
- Tealium: Strong data governance and privacy features.
- mParticle: Focuses on mobile data and real-time activation.
- BlueConic: Focuses on first-party data and consent management.
- Specialized/Niche CDPs:
- Optimove: Focuses on CRM marketing and customer lifecycle management.
- Lytics: Focuses on personalization and predictive analytics.
6. Future Trends in CDPs
- AI & Machine Learning: CDPs will increasingly leverage AI for predictive analytics, personalized recommendations, and automated segmentation.
- Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs): Focus on privacy-preserving data collection and analysis, like differential privacy and federated learning.
- Server-Side Tracking: Moving away from cookie-based tracking to server-side tracking for improved accuracy and privacy.
- Real-Time CDP: Demand for even faster data processing and activation for immediate personalization.
- Composable CDP: The ability to assemble a CDP from modular components, allowing for greater flexibility and customization.
- Integration with Generative AI: Using generative AI to create personalized content and experiences based on CDP data.
- Expansion Beyond Marketing: CDPs will be used more broadly across the organization, including sales, customer service, and product development.
7. Is a CDP Right for Your Business?
Consider a CDP if you:
- Have data scattered across multiple systems.
- Struggle to create a unified view of your customers.
- Want to deliver more personalized experiences.
- Need to improve marketing ROI.
- Are concerned about data privacy and compliance.
- Have a complex customer journey.
Resources for Further Learning
- The CDP Institute: https://www.cdpinstitute.org/
- Gartner Magic Quadrant for Customer Data Platforms: (Requires subscription)
- Forrester Wave™: Customer Data Platforms: (Requires subscription)
In conclusion, CDPs are a powerful tool for businesses looking to build stronger customer relationships and drive growth. Choosing the right CDP requires careful consideration of your specific needs and goals.