Raspberry Pi: A Comprehensive Overview
The Raspberry Pi is a series of small, affordable single-board computers (SBCs) developed by the Raspberry Pi Foundation in the UK. They’ve become incredibly popular with hobbyists, educators, and professionals alike, powering a huge range of projects. Here’s a breakdown covering everything from what it is to what you can do with it:
1. What is a Raspberry Pi?
- Single-Board Computer: Unlike a traditional desktop computer with separate components, everything is integrated onto a single circuit board. This makes it compact and efficient.
- Low Cost: Historically, the biggest draw. Models range from around $5 to $75+, making them accessible to a wide audience.
- Versatile: It’s a fully functional computer, capable of running a variety of operating systems, software, and performing many of the tasks a desktop computer can.
- GPIO Pins: A key feature! General Purpose Input/Output pins allow you to connect the Pi to external hardware like LEDs, sensors, motors, and more, making it ideal for physical computing projects.
2. Raspberry Pi Models (as of late 2023/early 2024)
Here’s a rundown of the most common models. The landscape changes frequently, so check the official Raspberry Pi website for the latest information:
- Raspberry Pi 5: The newest and most powerful. Significant performance improvements over previous generations. Features a faster processor, improved graphics, and more connectivity options. (Around $60-$80 depending on RAM)
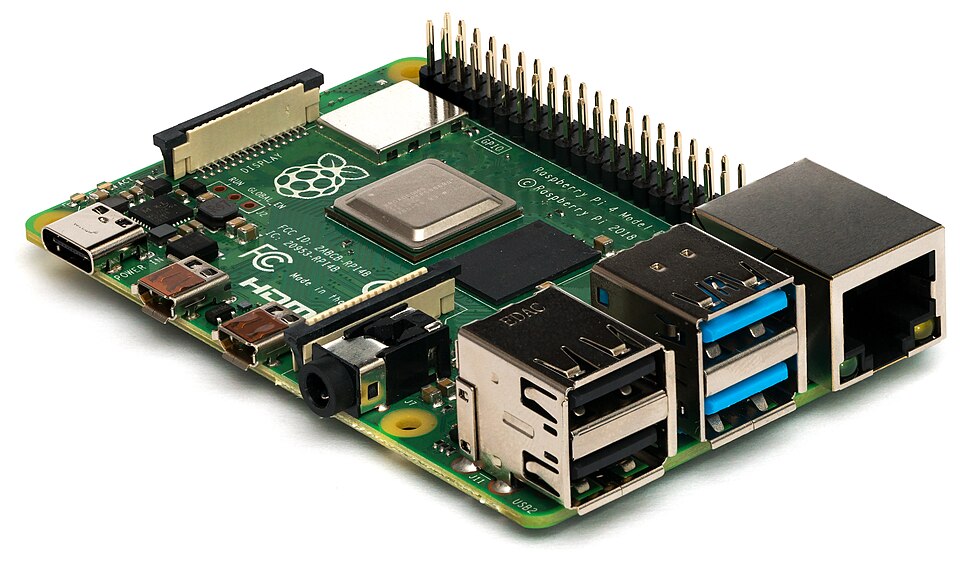
- Raspberry Pi 4 Model B: Still a very popular and capable choice. Available in various RAM configurations (2GB, 4GB, 8GB). Good for general computing, media centers, and more demanding projects. (Around $35-$75)
- Raspberry Pi 400: A Raspberry Pi 4 built into a keyboard. A convenient all-in-one solution for basic computing. (Around $70-$100)
- Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W: A tiny, low-cost option. More powerful than the original Zero, with built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. Great for embedded projects and portable applications. (Around $15-$20)
- Raspberry Pi Zero W: The original tiny Pi. Still useful for simple projects, but less powerful than the Zero 2 W. (Around $10-$15)
- Raspberry Pi Pico: A microcontroller, not a full computer. Focuses on real-time control and low-level programming. Extremely affordable. (Around $4-$6)
- Raspberry Pi Pico W: Like the Pico, but with added Wi-Fi connectivity. (Around $6-$8)
3. Key Specifications (varies by model – using Pi 4 Model B as an example)
- Processor: Broadcom BCM2711, Quad-core Cortex-A72 (ARM v8) 64-bit SoC @ 1.5GHz
- RAM: 2GB, 4GB, or 8GB LPDDR4 SDRAM
- Storage: MicroSD card slot for operating system and data storage.
- Connectivity:
- 2 x USB 3.0 ports
- 2 x USB 2.0 ports
- Gigabit Ethernet
- 802.11ac Wi-Fi
- Bluetooth 5.0
- 2 x Micro-HDMI ports (supports dual displays)
- 3.5mm audio jack
- GPIO: 40-pin GPIO header
- Power: 5V/3A via USB-C
4. Operating Systems
- Raspberry Pi OS (formerly Raspbian): The official and most popular operating system, based on Debian Linux. Optimized for the Raspberry Pi hardware.
- Ubuntu: A popular Linux distribution, available in desktop and server versions for the Pi.
- Other Linux Distributions: Many other Linux distributions are compatible, including Fedora, Arch Linux, and more.
- Windows 10 IoT Core: A version of Windows designed for embedded devices. (Limited support)
- RetroPie: A popular distribution for building retro gaming consoles.
- LibreELEC/Kodi: For creating media centers.
5. What can you do with a Raspberry Pi?
The possibilities are almost endless! Here are some popular projects:
- Media Center: Turn your TV into a smart TV with Kodi.
- Retro Gaming Console: Emulate classic video games with RetroPie.
- Home Automation: Control lights, thermostats, and other devices.
- Robotics: Build robots and control them with Python or other programming languages.
- Weather Station: Collect and display weather data.
- Security Camera: Create a DIY security system.
- Web Server: Host a website or blog.
- Network-Attached Storage (NAS): Create a personal cloud storage solution.
- Learning to Code: An excellent platform for learning Python, C++, and other programming languages.
- IoT (Internet of Things) Projects: Connect sensors and actuators to the internet.
- Digital Signage: Display information on a screen.
- Thin Client: Access remote desktops.
6. Resources for Learning
- Official Raspberry Pi Website: https://www.raspberrypi.com/ – Documentation, tutorials, and the official store.
- Raspberry Pi Foundation: https://www.raspberrypi.org/ – Educational resources and community information.
- Instructables: https://www.instructables.com/ – A wealth of Raspberry Pi projects.
- Hackster.io: https://www.hackster.io/ – Another great source for projects and tutorials.
- YouTube: Search for “Raspberry Pi” to find countless tutorials and project demonstrations.
- Reddit: r/raspberry_pi – A helpful community forum.
7. Things to Consider
- Power Supply: Use a good quality power supply that provides the correct voltage and amperage.
- MicroSD Card: Choose a fast and reliable microSD card.
- Case: Protect your Pi with a case.
- Accessories: You may need accessories like HDMI cables, keyboards, and mice.
- Learning Curve: While the Pi is accessible, some projects require programming knowledge and technical skills.
In conclusion, the Raspberry Pi is a powerful and versatile tool that can be used for a wide range of projects. Its affordability, ease of use, and large community make it an excellent choice for beginners and experienced makers alike.
Do you have any specific questions about the Raspberry Pi that you’d like me to answer? For example, are you interested in a particular model, a specific project, or learning how to get started? Let me know, and I’ll do my best to help!